[C#][.Net MVC] 7.驗證參數-DataAnnotations
使用者輸入欄位是網站最容易被攻擊的一個位置,養成良好的參數驗證可以避免很多資安的麻煩喔!
#什麼是DataAnnotations
DataAnnotations是.Net Framework 3.5之後提供的一個命名空間,裡面包含了一些基本的驗證Attribute,同時也提供客製化的方法,希望開發人員能透過簡單的加上Attribute即達到驗證的效果。
{
/// <summary>
/// 帳號
/// </summary>
[Required]
public string Account { get; set; }
}
#如何使用
我們透過修改先前的範例,嘗試將**UserSignUpParameter**的驗證從FluentValidation改成用MVC預設提供的DataAnnotations來達成,從修改中學習他是如何運作的。
重新審視一下需求
帳號
- 必填
- 必須包含@
密碼
- 必填
- 不得小於6個字元
RequiredAttribute
RequiredAttribute為DataAnnotations預設提供的驗證方式,目標是驗證該欄位是否為Null或Empty
// 摘要:
// 指定資料欄位值為必要。
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property | AttributeTargets.Field | AttributeTargets.Parameter, AllowMultiple = false)]
public class RequiredAttribute : ValidationAttribute
{
//
// 摘要:
// 初始化 System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.RequiredAttribute 類別的新執行個體。
public RequiredAttribute();
//
// 摘要:
// 取得或設定值,指出是否允許空字串。
//
// 傳回:
// true 如果允許空字串。否則, false。 預設值是 false。
public bool AllowEmptyStrings { get; set; } //
// 摘要:
// 檢查必要的資料欄位的值不是空的。
//
// 參數:
// value:
// 要驗證的資料欄位值。
//
// 傳回:
// true 如果驗證成功。否則, false。
//
// 例外狀況:
// T:System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.ValidationException:
// 資料欄位值為 null。
public override bool IsValid(object value);
}
從上述的程式碼可以看出它有提供**AllowEmptyStrings**的屬性可以設定,意義如同字面意思,可以**EmptyString**。
AllowEmptyStrings
我們先將Account掛上Required,並且指定屬性AllowEmptyStrings為True,執行看看繼承自Attribute的類別,在掛Attribute時可以省略後綴詞,所以可以看到程式碼只寫Required而不是RequiredAttribute
/// Parameter UserSignUp
/// </summary>
public class UserSignUpParameter
{
/// <summary>
/// 帳號
/// </summary>
[Required(AllowEmptyStrings =true)]
public string Account { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 密碼
/// </summary>
public string Password { get; set; }
}
當Account傳入為Null時
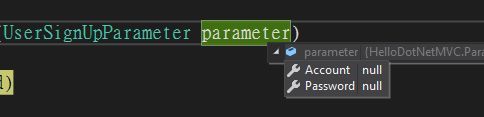
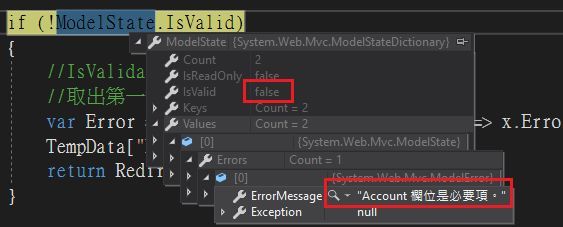
ModelState.IsValidate為False,在Values.Errors底下可以找到錯誤訊息Account 欄位是必要項。
接著改傳入空格
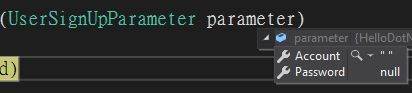
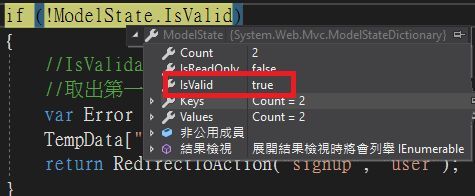
通過驗證
ErrorMessage
如果想修改錯誤的回傳訊息時,可以透過ErrorMessage來處理
/// 帳號
/// </summary>
[Required(ErrorMessage = "帳號為必填欄位")]
public string Account { get; set; }
或是
/// 帳號
/// </summary>
[Required(ErrorMessage = "{0}為必填欄位")]
public string Account { get; set; }
{0}的位置系統會自動帶入欄位名稱
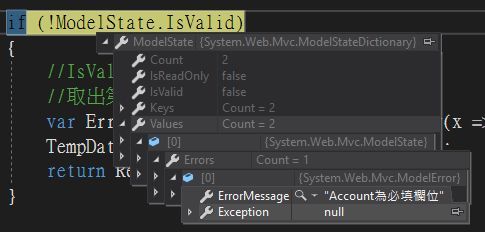
介紹完RequiredAttribute的基本用法後,目前程式碼如下
/// Parameter UserSignUp
/// </summary>
public class UserSignUpParameter
{
/// <summary>
/// 帳號
/// </summary>
[Required(ErrorMessage = "{0}為必填欄位")]
public string Account { get; set; } /// <summary>
/// 密碼.
/// </summary>
[Required(ErrorMessage = "{0}為必填欄位")]
public string Password { get; set; }
}
MinLengthAttribute
MinLengthAttribute是用來檢查屬性的最小字數,與MaxLengthAttribute為剛好相反的一組
// 摘要:
// 指定屬性中所允許之陣列或字串資料的最大長度。
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property | AttributeTargets.Field | AttributeTargets.Parameter, AllowMultiple = false)]
public class MaxLengthAttribute : ValidationAttribute
{
//
// 摘要:
// 初始化 System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.MaxLengthAttribute
類別的新執行個體。
public MaxLengthAttribute();
//
// 摘要:
// 初始化的新執行個體 System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.MaxLengthAttribute 類別根據 length
// 參數。
//
// 參數:
// length:
// 陣列或字串資料的最大容許長度。
public MaxLengthAttribute(int length); //
// 摘要:
// 取得陣列或字串資料所容許的最大長度。
//
// 傳回:
// 陣列或字串資料的最大容許長度。
public int Length { get; } //
// 摘要:
// 將格式套用到指定的錯誤訊息
//
// 參數:
// name:
// 要包含在格式化字串中的名稱。
//
// 傳回:
// 描述可接受之最大長度的當地語系化字串。
public override string FormatErrorMessage(string name);
//
// 摘要:
// 判斷指定的物件是否有效
//
// 參數:
// value:
// 要驗證的物件。
//
// 傳回:
// 如果此值為 null 或是小於或等於指定的最大長度,則為 true,否則為 false。
//
// 例外狀況:
// T:System.InvalidOperationException:
// 長度為零或小於 –1。
public override bool IsValid(object value);
}
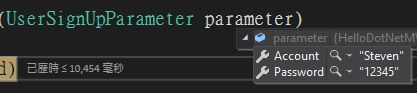
密碼最少應為6個字元設定方式,當然它同時也提供修改ErrorMessage的方法
{0}的位置系統會自動帶入欄位名稱
{1}的位置系統會帶入所設定的最小字元數字
/// 密碼.
/// </summary>
[MinLength(6, ErrorMessage = "{0}不得低於{1}個字元")]
public string Password { get; set; }
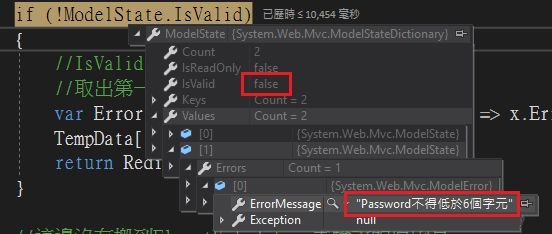
RegularExpression
Account還有一個需求是必須包含@字元,這時候可以透過預設提供的RegularExpression來達成需求
// 摘要:
// 指定 ASP.NET 動態資料的資料欄位值必須符合指定的規則運算式。
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property | AttributeTargets.Field | AttributeTargets.Parameter, AllowMultiple = false)]
public class RegularExpressionAttribute : ValidationAttribute
{
//
// 摘要:
// 初始化 System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.RegularExpressionAttribute
類別的新執行個體。
//
// 參數:
// pattern:
// 用來驗證資料欄位值的規則運算式。
//
// 例外狀況:
// T:System.ArgumentNullException:
// pattern 為 null。
public RegularExpressionAttribute(string pattern); //
// 摘要:
// 取得規則運算式模式。
//
// 傳回:
// 要比對模式。
public string Pattern { get; }
//
// 摘要:
// 取得或設定執行單一比對作業,直到作業逾時之前的時間 (以毫秒為單位)。
//
// 傳回:
// 執行單一比對作業的時間 (以毫秒為單位)。
public int MatchTimeoutInMilliseconds { get; set; } //
// 摘要:
// 格式化要顯示在規則運算式驗證失敗時的錯誤訊息。
//
// 參數:
// name:
// 造成驗證失敗的欄位名稱。
//
// 傳回:
// 格式化的錯誤訊息。
public override string FormatErrorMessage(string name);
//
// 摘要:
// 會檢查使用者輸入的值是否符合規則運算式模式。
//
// 參數:
// value:
// 要驗證的資料欄位值。
//
// 傳回:
// true 如果驗證成功。否則, false。
//
// 例外狀況:
// T:System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.ValidationException:
// 資料欄位值不符合規則運算式模式。
public override bool IsValid(object value);
}
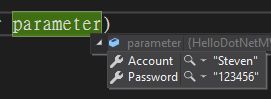
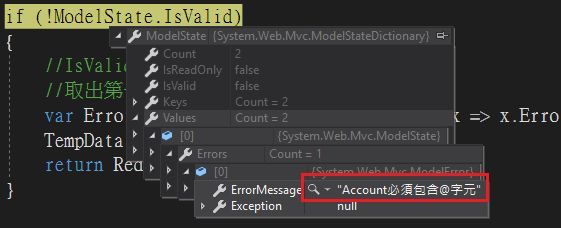
可以透過寫正規表示法的方式來驗證想驗證的屬性,一樣有ErrorMessage可供使用
/// 帳號
/// </summary>
[RegularExpression("[@]+",ErrorMessage ="{0}必須包含@字元")]
public string Account { get; set; }
其它Attribute
DataAnnotations還有提供一些預設的Attribute可以使用,篇幅有限就不一一介紹,有興趣的可以參考以下文章
[How To Validate MVC Model Using DataAnnotation Attribute] : 連結
[MSDN - ValidationAttribute 類別] : 連結
#客製
如果碰到一個驗證需要在多個地方使用,且預設沒有提供的話,這時候就可以透過自製驗證Attribute來解決,我們以字元需包含@為例
繼承ValidationAttribute
{
/// <summary>
/// Returns true if ... is valid.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value">要驗證之物件的值。</param>
/// <returns>
/// <see langword="true" /> 指定的值是否有效。否則, <see langword="false" />。
/// </returns>
public override bool IsValid(object value)
{
return base.IsValid(value);
}
}
Override IsValid Method
{
if (value == null)
{
return false;
}
var stringValue = value as string;
return stringValue.Contains("@");
}
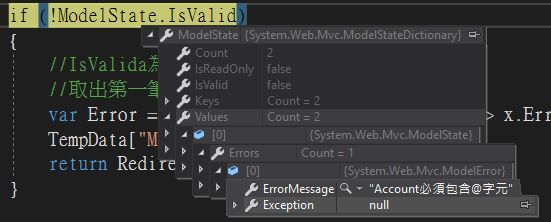
將原本的**RegularExpression**改成我們客製的MouseCharacters
/// 帳號
/// </summary>
[MouseCharacters(ErrorMessage ="{0}必須包含@字元")]
public string Account { get; set; }
實測會發現結果是一樣的
#比較FluentValidation
DataAnnotations其實使用起來相當方便,且只要知道如何客製ValidationAttribute基本上大部分情境都能解決,加上套用Attribute的方式算是相當親民的寫法。
但我本身基於單一職責的原則下,還是喜歡將驗證邏輯等方法分離到不同的Class管理,而這也正是FluentValidation套件的特性,不過這是見仁見智,就像大部分Pattern一樣,永遠不會有最好的解法,只要能花最小的成本解決需求,同時盡量不犧牲維護及擴充性,那就稱得上是好方法了。
最後,如果你喜歡我們的文章,別忘了到我們的FB粉絲團按讚喔!!
